What is SIEM?
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) is a software solution that aggregates and analyzes the activity of many different resources across the IT infrastructure.
SIEM collects security data from network devices, servers, domain controllers, etc. SIEM stores, normalizes, aggregates, and analyzes this data to discover trends, detect threats, and enable organizations to investigate any alerts.
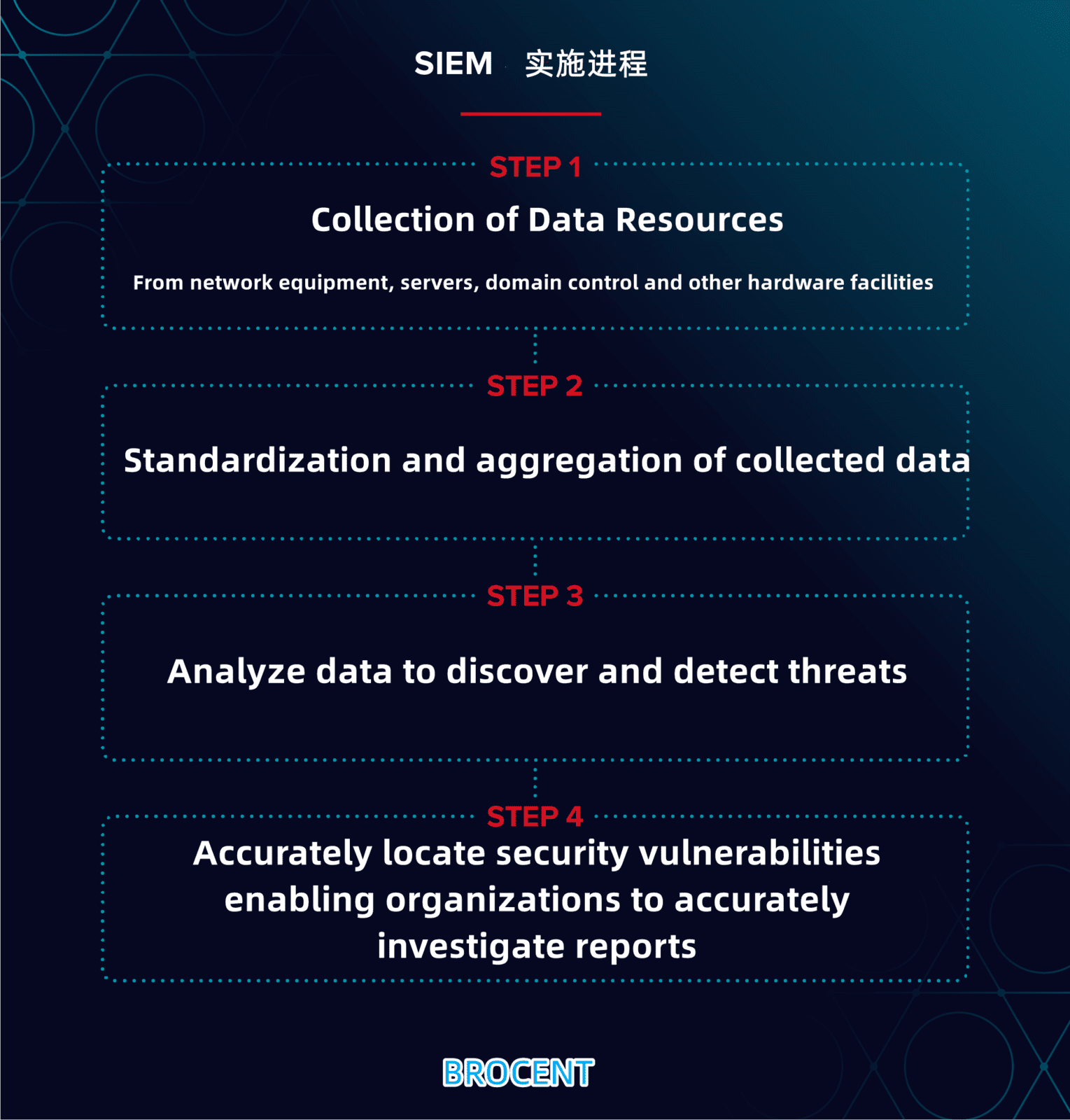
How does SIEM works?
SIEM provides two main functions for incident response teams
At its core, SIEM is a data aggregator, search and reporting system. SIEM collects large amounts of data from your entire network environment, consolidates that data and makes it accessible to humans. With categorized and laid out data at your fingertips, you can study data security vulnerabilities in as much detail as needed.
Security information and event management functions
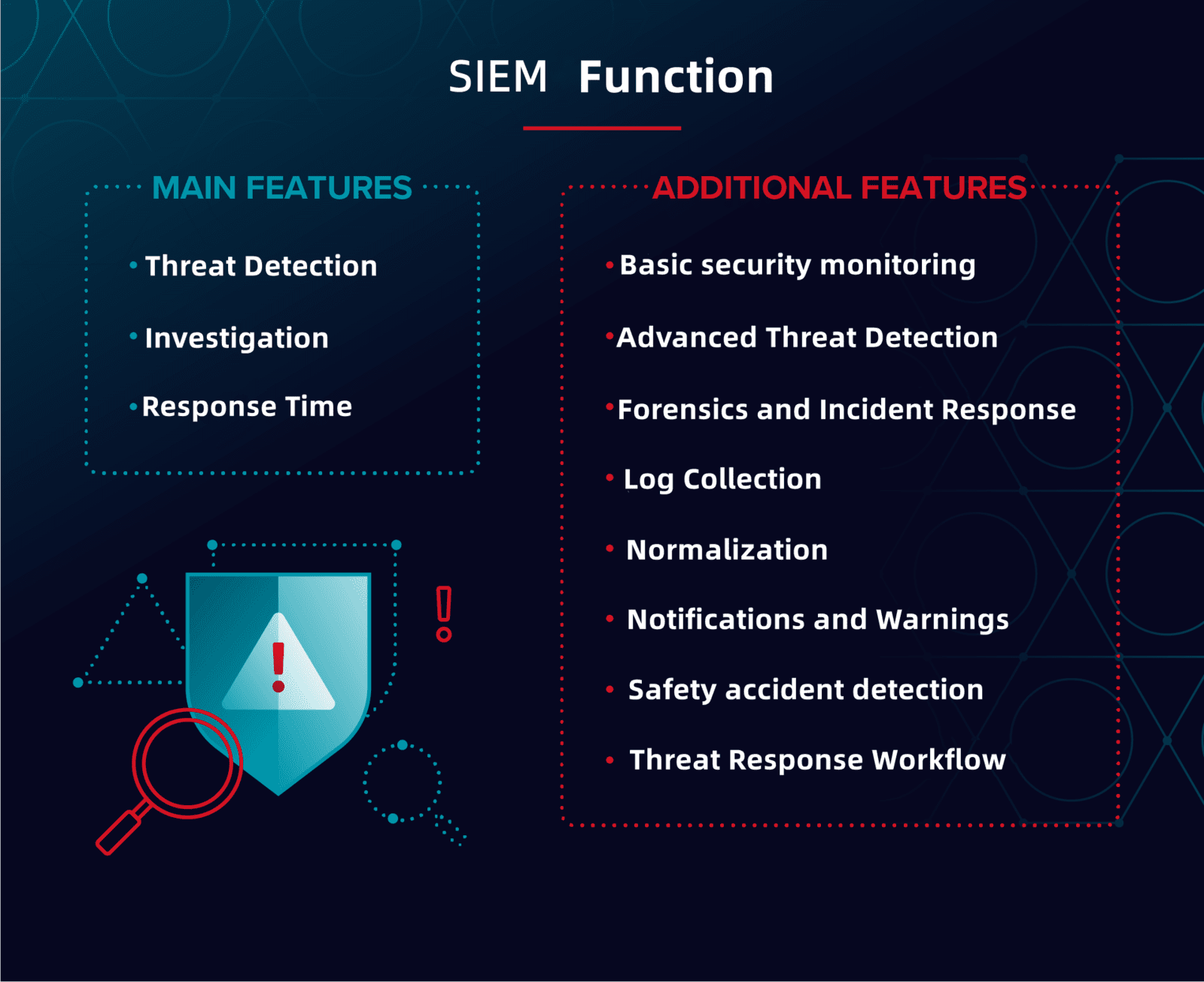
Defined three key functions of SIEM (threat detection, investigation, and response time)
-- Other features and capabilities you would typically see in the SIEM marketplace, including.
Defined three key functions of SIEM (threat detection, investigation, and response time)
-- Other features and capabilities you would typically see in the SIEM marketplace, including.

SIEM in the Enterprise
Some customers find that they need to maintain two separate SIEM solutions to get the most value for each purpose, as SIEMs can be very noisy and resource intensive: they typically prefer one for data security and one for compliance.
In addition to the primary use case of SIEM for logging and log management, organizations use their SIEMs for other purposes. Another use case is to help demonstrate compliance with regulations such as HIPAA, PCI, SOX, and GDPR.
SIEM tools also aggregate data that can be used for capacity management projects. You can track bandwidth and data growth over time for planning growth and budgeting purposes. In the capacity planning world, data is key, and understanding your current usage and trends over time allows you to manage growth and avoid large capital expenditures as a reactionary measure rather than a preventative one.




